تقدم حاسبة Windows(Windows Calculator) الجديدة عمليات حسابية أكثر دقة من أي وقت مضى ولديها أيضًا واجهة جديدة وقوية. وهو الآن يدمج الحسابات القياسية الأساسية مع البرمجة والحسابات العلمية والإحصاءات. علاوة على ذلك ، هناك أيضًا ميزات أخرى مفيدة للغاية: أشياء مثل حساب الرهن العقاري(mortgage calculation) ، ومحول متعدد الوظائف ، وعدد قليل من الخيارات الأخرى التي تستحق نصيبها من الاهتمام. في هذه المقالة سأقدمهم واحدًا تلو الآخر وأشارك أيضًا بعض سيناريوهات الاستخدام الممكنة.
أين تجد الآلة الحاسبة(Calculator) في Windows 7 و Windows 8
في Windows 7 ، يمكنك الوصول إليه من خلال الانتقال إلى Start Menu - > Accessories -> Calculator .
يمكن أيضًا فتح الحاسبة عن طريق كتابة الآلة الحاسبة (Calculator)أو الحاسبة(calculator) في مربع(calc) البحث في قائمة (search box)ابدأ(Start Menu) (في Windows 7 ) أو في شاشة البدء(Start) (في Windows 8 ) وفتح نتيجة البحث(search result) المناسبة .
يمكن العثور على ملفه التنفيذي في هذا الموقع "C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe":.
طرق الحساب
على الرغم من أن لديها إصدارًا مختلفًا في Windows 8 ، مقارنةً بـ Windows 7 ، فإن الآلة الحاسبة(Calculator) هي نفسها في كلا نظامي التشغيل. تبدو الواجهة كما هي وميزاتها متطابقة.
تحتوي الآلة الحاسبة(Calculator) على 4 أوضاع رئيسية يمكنك من خلالها إجراء العمليات الحسابية:
- الوضع القياسي.
- الوضع العلمي.
- وضع البرمجة.
- وضع الإحصاء.
في الأقسام أدناه سأصف كل منهم وأشرح ما يفعلونه وكيفية استخدامه.
الوضع القياسي
عند فتح الحاسبة(Calculator) لأول مرة ، سيتم تحديد الوضع القياسي(Standard) افتراضيًا. هذا الوضع هو أفضل مكافئ لآلة حاسبة الجيب(pocket calculator) العادية . يمكنك استخدام قيم أرقام لوحة المفاتيح أو لوحة المفاتيح (مع تنشيط مفتاح (keyboard number)Num ) أو الماوس لإجراء العمليات الحسابية.
مثال:(Example:) تحتاج إلى اختيار الأرقام التي تريد إجراء العمليات الحسابية بها والعملية على هذه الأرقام. لذلك ، إذا كنت ستقوم بضرب بسيط ، فستضغط على الرقم الأول ، والعملية (* علامة الضرب) والرقم الثاني. في نهاية عملية الحساب(calculation process) ، يمكنك إما الاستمرار في إضافة عملية جديدة إلى تلك النتيجة أو النقر فوق(result or click) علامة المساواة للحصول على النتيجة النهائية(end result) .
وضع المبرمج
يوفر هذا الوضع إمكانية القيام بعمليات باستخدام القواعد(bases) (ثنائي ، ثماني ، سداسي عشري ، عشري). يمكنك تحويل القيم من قاعدة إلى أخرى. على سبيل المثال ، يمكنك التحويل من نظام رقمي (number system)أساسي(base two) (ثنائي - 0 ، 1) إلى نظام رقم أساسي عشرة(base ten number system) (عشري 0-9). يوفر هذا الوضع أيضًا المساعدة في عمليات البت المنطقية ( XOR و OR و AND ، إلخ(AND etc) ).
للوصول إلى هذا الوضع ، انقر فوق القائمة " عرض(View) " وحدد خيار " مبرمج(Programmer) " .

مثل الإصدارات السابقة ، ترتبط المفاتيح التي تستخدمها بالقاعدة. على سبيل المثال ، لا يمكن الوصول إلى الأزرار A - F إلا إذا قمت بالتحقق من أنها تعمل بقيم سداسية عشرية. الأزرار الأخرى شائعة بالفعل للمبرمج أو يجب أن تكون كذلك. تتراوح من خلال جدول لوح الألوان XOR(XOR table) ،٪ - المعامل ، التحول والتغيير من العشري إلى السداسي العشري أو النتائج الثنائية. أيضًا ، يتم عرض القيم التي تحصل عليها كأعداد صحيحة (الأرقام الطبيعية ، أي 16/3 ستساوي 5).
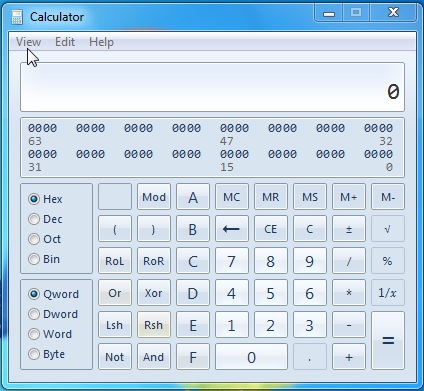
مثال:(Example:) إذا كان عليك تحويل قيمة ثنائية مثل 1011 إلى قيمتها العشرية ، يمكنك كتابة الرقم والنقر ببساطة على مربع(radio box) الاختيار العشري . يدويًا ، ستكون هذه العملية طويلة إلى حد ما وربما تسبب مشاكل خطأ إذا لم تستوعب المفهوم بالكامل.

الوضع العلمي
يقدم هذا الوضع القليل من الابتسامة لأي شخص يتابع العمليات الحسابية أو العمليات الحسابية العلمية الأخرى. يتراوح العرض من X الأساسي الخاص بك إلى قوة وظائف (X to the power of)cos أو sin أو pi الأكثر فائدة .
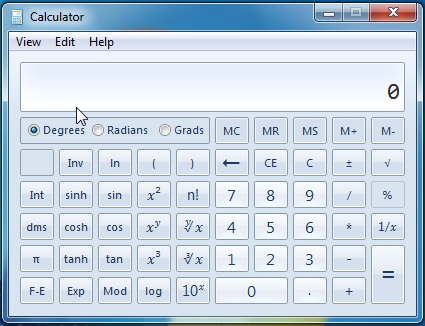
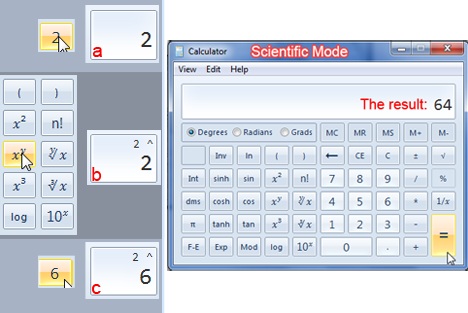
مثال:(Example:) كما فعلت من قبل في الوضع القياسي ، لإجراء عملية ، انقر فوق رقم ، متبوعًا بعملية ثم ضع الرقم الثاني.
وضع الإحصاء
يقدم هذا الوضع الخيارات المتعلقة بالإحصاءات. على الرغم من أنها لا تحتوي على العديد من الوظائف مثل الأوضاع الأخرى ، إلا أنها مرحب بها أكثر. يمكنك استخدام وظائف مثل مجموع الأرقام ومجموع الأرقام للأس لتكوين الإحصاء حساب التفاضل والتكامل.
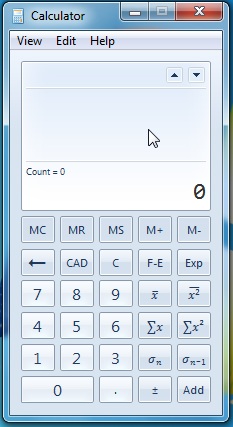
الضغط على C ، في الحالة الوحيدة لوضع الإحصاء ، يحذف القيمة الحالية المعبر عنها. يمسح CAD(CAD) جميع القيم من مجموعة البيانات . مجموعة البيانات هي قائمة الأرقام المضافة. مجموعة البيانات هي القائمة التي ستؤدي من خلالها عمليات مختلفة.
مثال:(Example:) للقيام بعملية في وضع الإحصائيات ، عليك أن تضع القيم. سيتم وضع كل قيمة بعد كتابتها في مجموعة البيانات بالنقر فوق الزر " إضافة ". (ADD)بعد وضع جميع القيم المطلوبة في قائمة مجموعة البيانات(dataset list) ، يمكنك النقر فوق العملية المطلوبة.

استخدام التاريخ(History) مع أوضاع الحساب(Calculation Modes)
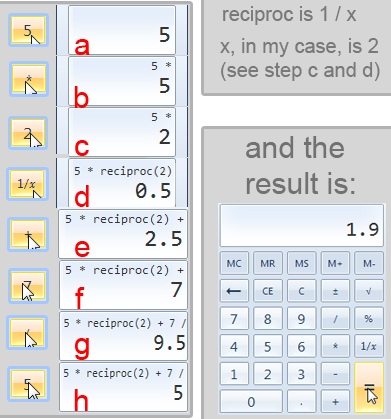
يتجاوز هذا الخيار القيم المفيدة المحفوظة في الذاكرة. يمكن استخدامه بالذهاب إلى File -> History وهو متاح لجميع الأوضاع باستثناء وضع الإحصائيات. الاسم يقول كل شيء ، لكنه أقوى مما يبدو. أصبح اللعب بالصيغ المعقدة أمرًا بسيطًا. يمكنك إجراء عملية حسابية ، وعند الانتهاء ، انقر فوق المساواة للحصول على النتيجة. سيؤدي هذا إلى إدخال النتيجة في قائمة المحفوظات(History) . إذا أجريت عملية حسابية أخرى وتحتاج إلى النتيجة أو القيم(result or values) السابقة من تلك النتيجة ، فما عليك سوى البحث في القائمة والاطلاع على هذه القيم. هذا إلى جانب حقيقة أنه يمكنك بسرعة إعادة الحسابات السابقة مما يجعل الآلة الحاسبة تتجاوز(calculator surpass) أي آلة حاسبة على الإنترنت(calculator offering)التي قد يستخدمها المرء كسلعة. للوصول إلى هذا الخيار ، تأكد من أنك في وضع صالح (الكل باستثناء وضع الإحصائيات).

خيارات أخرى في الحاسبة
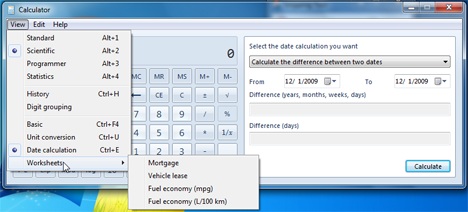
تتضمن الآلة الحاسبة(Calculator) الآن أدوات أخرى خارج نطاق أوضاع الحساب. هم أكثر ارتباطًا بالضروريات اليومية. أشياء مثل تحويل الوزن الخفيف أو حساب المسافة من يوم محدد إلى آخر. الذهاب إلى أبعد مما قد تحتاجه عادةً من الآلة الحاسبة ، فإنه يوفر أيضًا مساعدتك في حساب قيم الرهن العقاري وتأجير السيارة واستهلاك السيارة(vehicle lease and car consumption) .
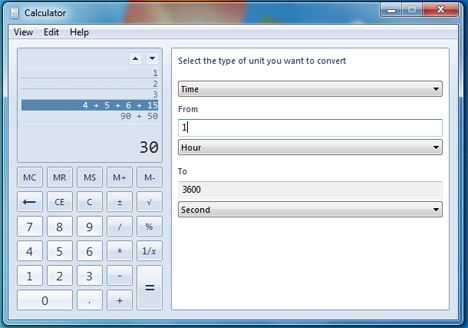
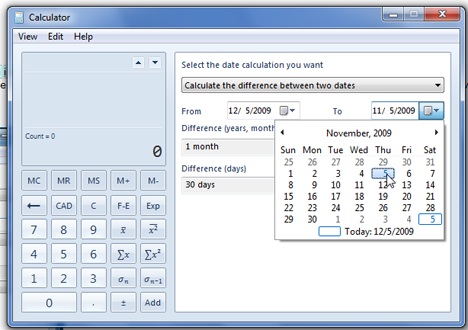
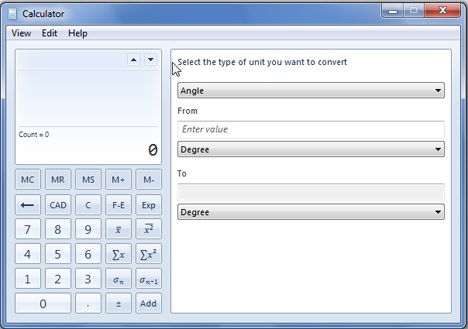
يجب عليك تحديد نوع التحويل (على سبيل المثال: الوقت) ، والقياس من (From) الوحدة(unit measurement) (مثل الساعة(Hour) ) ، ووحدة القياس إلى(To) (مثل الثانية).
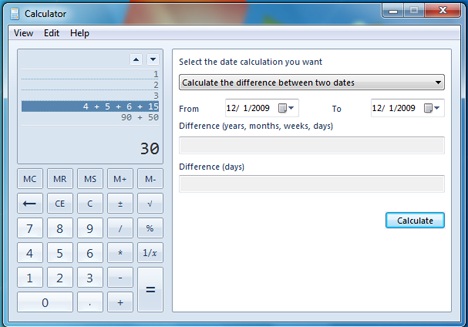
حدد التواريخ (من وإلى) لمعرفة الفرق بينهما. يمكنك أيضًا كتابة عدد الأيام والشهور (وما إلى ذلك) يدويًا للطرح (أو الإضافة) من التاريخ والاطلاع على النتيجة النهائية. يتم ذلك عن طريق النقر فوق "احسب الفرق بين تاريخين"('Calculate the difference between two dates') واختيار الخيار الثاني المحدد.
Worksheets - These are options offered for real life calculations. Whether you want to calculate mortgage, vehicle lease or car consummation (American or European measurement), the calculator offers it all in the worksheets place.
النصائح والحيل
غالبًا ما أتفاجأ من عدم استخدام بعض الأدوات المساعدة من الآلة الحاسبة العادية. الموضوع الذي أشير إليه هو الذاكرة والوظائف المفيدة الأخرى المضمنة في الآلة الحاسبة.
MC (Memory Clear or Clean) - clears the memory of any stored number leaving only the null or zero number in memory.
MR (Memory Reminder or Recalled) - tells the calculator to show the number present in memory.
MS (Memory Store or Set) - this takes the number present in the results and stores it in the memory. Previous calculation stored in memory will be deleted.
M+ (Add to memory) - formula> value stored in memory + current value = new value stored.
M- (Subtract from memory) - formula> value stored in memory - current value = new value stored.
C - Clear all calculations that are currently made.

The Back Arrow or Backspace - present on Windows Calculator but not present on a pocket calculator. This option deletes the last typed number from the current value. This option can be used by clicking on the Back Arrow or by pressing the Backspace key.
Using numerical values from the keyboard makes the calculation faster. You can also use the * key to quickly multiple, the minus key "-", the plus key "+", the divisible by "/" or the equal key "=".
Although this has nothing to do with notations, you can click on the Edit-> Copy to copy the value to clipboard.
Going to the help page for calculator reveals useful keyboard shortcuts for use with functions or options.
خاتمة
التغييرات في طريقة ظهورها والخيارات المتوفرة بها ، تجعل الآلة الحاسبة(Calculator) تبدو وكأنها قد تم إنشاؤها مع وضع وظائف سريعة وخفيفة الوزن في الاعتبار. تعمل جميع الميزات معًا بشكل جيد ويتم الانتقال بين الخيارات بسهولة بالغة. في النهاية ، إذا كانت لديك مشاكل أو أسئلة أو كنت تعرف فقط بعض النصائح والحيل الرائعة حول هذه الأداة ، فلا تتردد في مشاركتها معنا في تعليق.
The Calculator in Windows 7 & Windows 8 - A Tool for the Geek in You!
The nеw Windows Calculator offers more precise calculations than ever and it also has a new and powerful interface. It now integrates the basic standard calculations with programming, scientific calculations and statistics. Beyond this, there are also other features which are very useful: things like mortgage calculation, a multifunctional converter and a few more options which deserve their share of attention. In this article I will present them one by one and also share some possible usage scenarios.
Where to Find the Calculator in Windows 7 & Windows 8
In Windows 7 you can access it by going to Start Menu - > Accessories -> Calculator.

The Calculator can be opened also by typing calculator or calc in the Start Menu search box (in Windows 7) or in the Start screen (in Windows 8) and opening the appropriate search result.
Its executable can be found in this location: "C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe".
Calculation Modes
Even though it has a different version in Windows 8, compared to Windows 7, the Calculator is the same in both operating systems. The interface looks just the same and its features are identical.
The Calculator has 4 main modes with which you can do calculations:
- The Standard Mode.
- The Scientific Mode.
- The Programming Mode.
- The Statistics Mode.
In the sections below I will describe each of them and explain what they do and how to use them.
The Standard Mode
When you first open the Calculator, the Standard mode will be selected by default. This mode is the better equivalent of the normal pocket calculator. You can use the keyboard number values, the keypad (with the Num key activated) or the mouse to make calculations.

Example: You need to choose the numbers with which you want to do calculations and the operation on those numbers. So, if you were to do a simple multiplication you would click on the first number, the operation ( * multiply sign ) and the second number. At the end of the calculation process you can either continue to add a new operation to that result or click on the equal sign to get the end result.

The Programmer Mode
This mode offers the possibility to do operations with bases (binary, octal, hexadecimal, decimal). You can convert values from one base to another. For example, you can convert from a base two number system (binary - 0, 1) to a base ten number system (decimal 0-9). Also, this mode offers to help with logical bit operations (XOR, OR, AND etc).
To access this mode click on the View menu and select the Programmer option.

Like previous versions, the keys you use are related to the base. For example, the A - F buttons are only accessible if you check to work in hexadecimal values. The other buttons are or should be already common for a programmer. Ranging through the palette XOR table, % - modulus, shifting and changing from decimal to hexadecimal or binary results. Also, the values you get are shown as integers (natural numbers, meaning 16/3 will equal to 5).

Example: If you have to transform a binary value like 1011 to its decimal value you would type the number and simply click on the decimal radio box. Manually, this process would be rather lengthy and probably bring error problems if you don't fully grasp the concept.

The Scientific Mode
This mode offers a bit of a smile to any person who pursues mathematical or other scientific calculations. The offering ranges from your basic X to the power of to the more useful cos, sin or pi functions.

Example: Like you did before in the standard mode, to do an operation, click on a number, followed by an operation then put the second number.

The Statistics Mode
This mode presents options related to the statistics. Although it doesn't have many functions like other modes, they are more than welcomed. You can use functions like sum of numbers, sum of numbers to the power to make statistics calculus.

Pressing the C, in the sole case of statistics mode, deletes the current value expressed. The CAD clears all the values from the dataset. The dataset is the list of added numbers. The dataset is the list with which you will perform different operations.
Example:To do an operation in the statistics mode, you have to place the values. Each value after has been typed will be placed in the dataset by clicking the ADD button. After you have placed all the needed values in the dataset list, you can click on the wanted operation.

Using History with Calculation Modes
This option goes beyond the useful values kept in memory. It can be used by going to File -> History and it is available for all the modes except the statistics one. The name says it all, however it is more powerful than it sounds. Playing around with complex formulas is made simple. You can do a calculation and, when done, click on the equal to have the result. This will make the result to enter into the History list. If you do another calculation and need the previous result or values from that result you just look up into the list and see those values. This coupled with the fact that you can quickly reedit former calculations makes the calculator surpass any online calculator offering that one might use for commodity. To access this option, make sure you are in a valid mode (all except statistics mode).

Other Options in the Calculator
The Calculator calculator now includes other tools that are beyond the scope of the calculation modes. They are more related to everyday necessities. Things like light weight conversion or calculating the distance from one specified day to another one. Going a little further than what you would normally need from a calculator, it also offers to help you with calculating mortgage values, vehicle lease and car consumption.




You have to select the type of transformation (example: Time), the From unit measurement (like Hour), and the To measurement unit (like Second).

Select the dates (from and to) to see the difference between them. You can also manually type a number of days, months (etc.) to subtract (or add) from a date and to see the final result. This is done by clicking on the 'Calculate the difference between two dates' and selecting the second given option.
Worksheets - These are options offered for real life calculations. Whether you want to calculate mortgage, vehicle lease or car consummation (American or European measurement), the calculator offers it all in the worksheets place.
Tips and tricks
I am often surprised of how unused some utilities are from a regular calculator. The subject I am referring to is the memory and other useful functions included in a calculator.
MC (Memory Clear or Clean) - clears the memory of any stored number leaving only the null or zero number in memory.
MR (Memory Reminder or Recalled) - tells the calculator to show the number present in memory.
MS (Memory Store or Set) - this takes the number present in the results and stores it in the memory. Previous calculation stored in memory will be deleted.
M+ (Add to memory) - formula> value stored in memory + current value = new value stored.
M- (Subtract from memory) - formula> value stored in memory - current value = new value stored.
C - Clear all calculations that are currently made.

The Back Arrow or Backspace - present on Windows Calculator but not present on a pocket calculator. This option deletes the last typed number from the current value. This option can be used by clicking on the Back Arrow or by pressing the Backspace key.
Using numerical values from the keyboard makes the calculation faster. You can also use the * key to quickly multiple, the minus key "-", the plus key "+", the divisible by "/" or the equal key "=".
Although this has nothing to do with notations, you can click on the Edit-> Copy to copy the value to clipboard.
Going to the help page for calculator reveals useful keyboard shortcuts for use with functions or options.
Conclusion
The changes in the way it looks and the options it has, make the Calculator feel like it has been built with quick lightweight functionality in mind. All features work well together and the transitions between options are done very easily. In the end, if you have problems, questions or you just know some great tips and tricks about this tool, don't hesitate to share them with us in a comment.

















